Pediculosis pubis (Pubic lice) and Genital scabies are the cause of genital infestations. An infestation is an invasion of insects on a place like a house or an attack by insects on a plant.
Pediculosis pubis (Pubic lice)
The crab louse Phthirus pubis causes an infestation known as pediculosis pubis, sometimes referred to as pubic lice. The species responsible for head lice is not the same as this. Course hairs, including body hair (including beards) and, less often, eyebrows and eyelashes, are what the adult louse cling to. Insect Phthirus pubis suckers blood. Round, about 1–2 mm length, it is dark grey or brown in hue.

Life cycle: Five days to five weeks make up the incubation stage. The adult female deposits her eggs, or nits, at the base of the hairs, which hatch out in seven days on average. The eggs cling firmly to the hairs
Transmission: occurs when two people come into close physical contact. To live, the louse needs a human host, and it is unlikely to survive more than a day away from one.
Signs and symptoms
The most prevalent sign is pruritis, particularly of the vaginal region. The lice’s saliva and excrement irritate the skin.
A person may have no symptoms at all or may see lice or nits on their body.
Maculae caeruleae, tiny blue macules, are visible when bleeding into the skin at feeding sites has occurred.
Diagnosis
Finding adult lice or nits on body hair is how the disease is identified.
Usually, a naked eye assessment will do; but, suspected lice or eggs can be seen under low-power light microscope.
Management
General: provide a STI screening. Laundry bed linen and clothes at 50°C is recommended. Till the index patient and/or partner(s) have received treatment, avoid making close physical contact.
Treatments advised: Since alcoholic preparations might irritate excoriated skin, aqueous preparations and dermal cream are suggested. After seven days, a second application—a 0.5% aqueous solution of malathion—should be made over the entire body and rinsed off after at least two hours, ideally twelve. OR – Apply a 5% cream rinse of permethrin to the entire body and rinse it off after 12 hours. Choosing of treatment during pregnancy or nursing
Eyelash treatment: Closed eyes can have 1% permethrin lotion administered for ten minutes. Alternatively, to suffocate adult lice and nymphs (immature lice), lashes and eyelash roots can be treated with soft paraffin eye ointment for 8–10 days without causing any eye irritation.
Partner notification: partners who are still together as well as those who were in the last three months should be looked at and treated.
Follow-up: check again a week after the last treatment, and if live lice are still present, try another treatment. Dead nits could nonetheless be clinging to hairs. A nit comb will help to eradicate them. Patients need to know that even after effective treatment, pruritus may linger for a week or more.
Drugs like antihistamines can assist with this.
Genital scabies
Background
The parasite mite Sarcoptes scabiei is to blame for this infection. Over their 4–6 week lives, the female mites burrow into the skin and deposit one to three eggs every day. In three to four days after hatching, the larvae emerge onto the skin and dig fresh burrows. Food for the mites is lysed skin tissue and lymph. Only 72 hours is the longest a mite can live apart from its host.
It can infect any part of the body, including the hands, and is spread by skin-to-skin contact (mites are transferred after around 10–20 minutes of close contact).
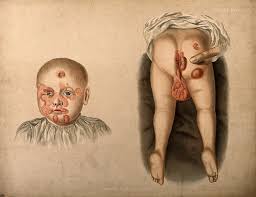
Signs and symptoms
- The reason of generalized pruritis, particularly at night, is a hypersensitivity reaction brought on by mite excrement absorbed into skin capillaries.
- One can get a secondary infection from excoriation where mites have burrowed, there may be silvery lines in the skin or genital papules or nodules.
- The wrists, extensor surfaces of elbows, the genitalia, and, in women, the area around the nipples are classical areas.
Diagnosis - Usually, the common indications and symptoms lead to a clinical diagnosis.
- Mites can be seen by light microscopy on scrapings taken from burrows. One could mistake the appearance for eczema
Management - Broadly speaking If there is a chance of sexual acquisition, a STI screening should be offered.
- Bed linen and clothing should be washed at a temperature of at least 50°C. Till the index patient and partner(s)/near household members have received treatment, close bodily contact should be avoided.
- Method of Treatment Application of a 0.5% aqueous solution or a 5% dermal cream (safe during pregnancy or nursing) to the entire body starting at the neck and washing off after 12 hours (permethrin) or 24 hours (Malathion). Treat again after seven days. Itching may last for a few weeks following effective treatment. Antihistamines can help control symptoms.
- Notify your partner and track down and handle any recent sexual and home connections as well as those from the last two months.
- If more burrows show up, follow up by retreating.
- One variation that strikes the elderly or immunocompromised (such as those with HIV infection) is called Norwegian scabies. Thousands of mites abound in hyperkeratotic crusting lesions that form. Very contagious is it. At this
You can also follow

