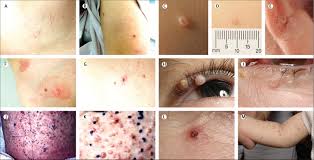
Anogenital warts and human papillomavirus infection
The human papillomavirus (HPV) that is spread through vaginal contact is the most common sexually transmitted virus in the world. Anogenital warts, also known as condylomata acuminata or genital warts, cause a lot of pain and illness and cost a lot of money to treat. Aetiology and epidemiology Diagnosis First invitation (age) 25 years Routine … Read more