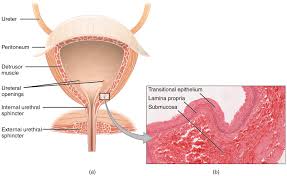
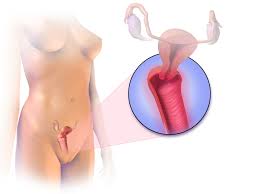
Vulvovaginal candidiasis
With women of reproductive age, vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) is common. About 75% of women will at some time in their life have symptomatic VVC. Etiology For 80–92% of VVC instances, Candida albicans is to blame. The species C. glabrata, C. tropicalis, and C. krusei are responsible for the remaining occurrences. If symptoms are absent, isolation … Read more