The Link Between Obesity and Chronic Diseases
Obesity has become a major global health issue, affecting millions of people. It is not just about excess body weight; it significantly increases the risk of chronic diseases that can reduce life expectancy and quality of life. Studies show that obesity is directly linked to conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, and even some types of cancer. Understanding how obesity contributes to these health problems is essential for preventing long-term complications.
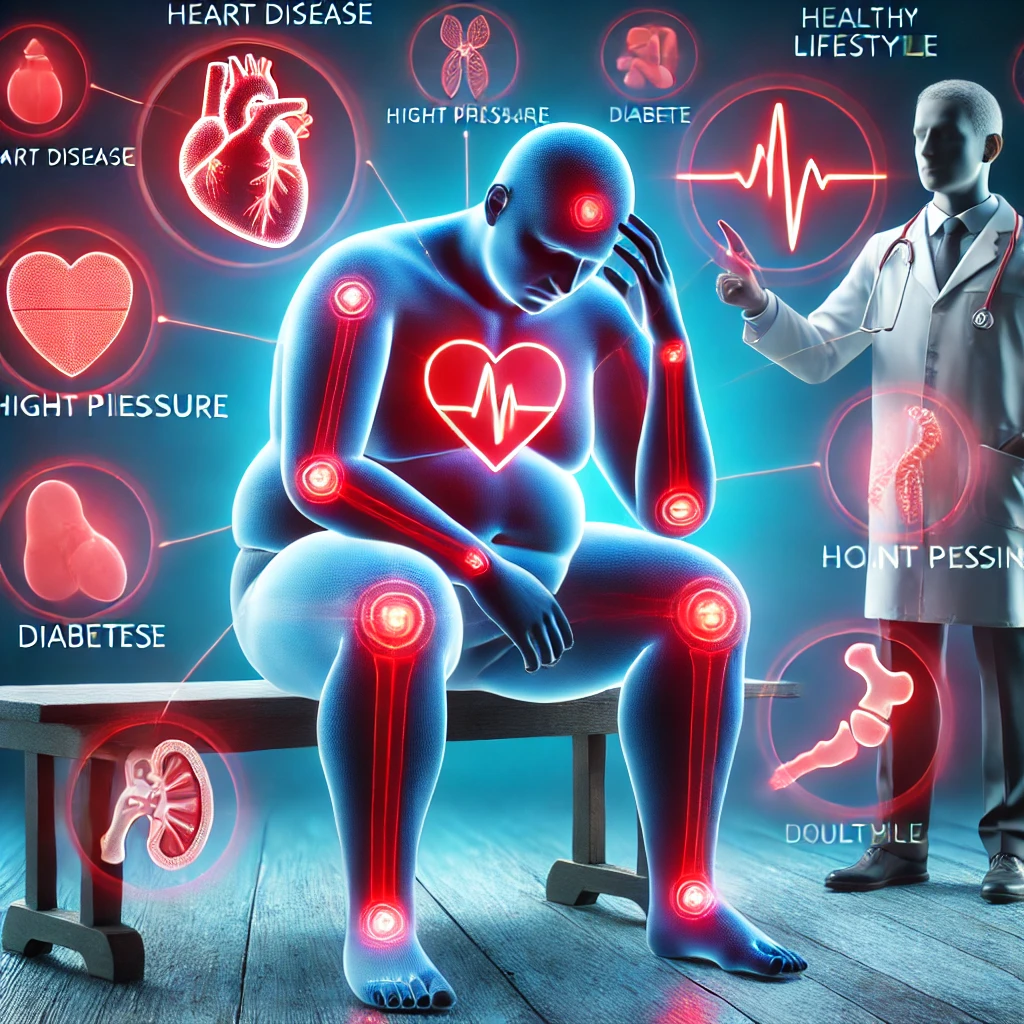
How Obesity Increases the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Obesity affects almost every system in the body, leading to chronic diseases that require lifelong management. Excess fat causes hormonal imbalances, increases inflammation, and puts extra strain on vital organs. Here’s how obesity contributes to various diseases:
- Heart Disease and Stroke – Obesity raises bad cholesterol (LDL) and lowers good cholesterol (HDL), leading to clogged arteries. High blood pressure and excess fat around the heart can result in heart attacks and strokes.
- Type 2 Diabetes – Obese individuals are at a higher risk of insulin resistance, which prevents the body from processing sugar properly. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels and, eventually, chronic diseases like diabetes.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) – Carrying excess weight forces the heart to work harder, increasing the risk of high blood pressure, a leading cause of heart disease and kidney problems.
- Liver Disease – Fat accumulation in the liver can lead to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), which may progress to liver failure if left untreated.
- Joint Problems and Arthritis – Excess weight puts pressure on the joints, leading to osteoarthritis and reduced mobility.
How to Prevent Obesity-Related Chronic Diseases
The good news is that obesity-related chronic diseases can often be prevented or managed through lifestyle changes. Here are some essential tips:
Healthy Eating Habits – A balanced diet with whole grains, lean proteins, and fresh vegetables can help manage weight.
Regular Physical Activity – Exercise for at least 30 minutes a day to improve metabolism and cardiovascular health.
Weight Management – Monitor portion sizes and avoid processed foods that lead to excessive calorie intake.
Adequate Sleep – Poor sleep patterns can contribute to weight gain and hormonal imbalances.
Conclusion
The connection between obesity and chronic diseases is undeniable. However, making small, consistent lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of these health problems. Prioritizing a balanced diet, regular exercise, and healthy habits can lead to a longer, healthier life. Preventing obesity is the key to reducing the global burden of chronic diseases and improving overall well-being.ng.

